“LEASE VALUE CALCULATOR FORMULA = What they want you to know ÷ WHAT WE KNOW”
What is a Cell Site? How Do Cell Sites Work?
A Cell Site is the backbone of wireless telecommunications and life as we know it.
Stop and imagine, where would be today, without cell sites? In an era where staying connected is an integral part of our daily lives, understanding the infrastructure that enables seamless communication is crucial. Cellular communication sites are everywhere. As 3G technology evolved into the fourth generation or 4G somewhere in 2007, we ditched our Blackberry’s for the iPhone and eventually other smart phones, and life has never been the same. Did you know that 70% of emergency E-911 calls in the United States are made from a mobile device? That’s around 400,000 emergency phone calls daily that pass through a cell site network in one way or another.
As much as the smartphone was revolutionary, at the heart of wireless telecommunications lies the cell site, not the cellular phone. A cell site is a network of interconnected components that facilitate the transmission of voice, data, and multimedia between cellular devices. Let’s dig into what makes up a cell site, how cell towers they operate, how they communicate, and the technologies that make them work.
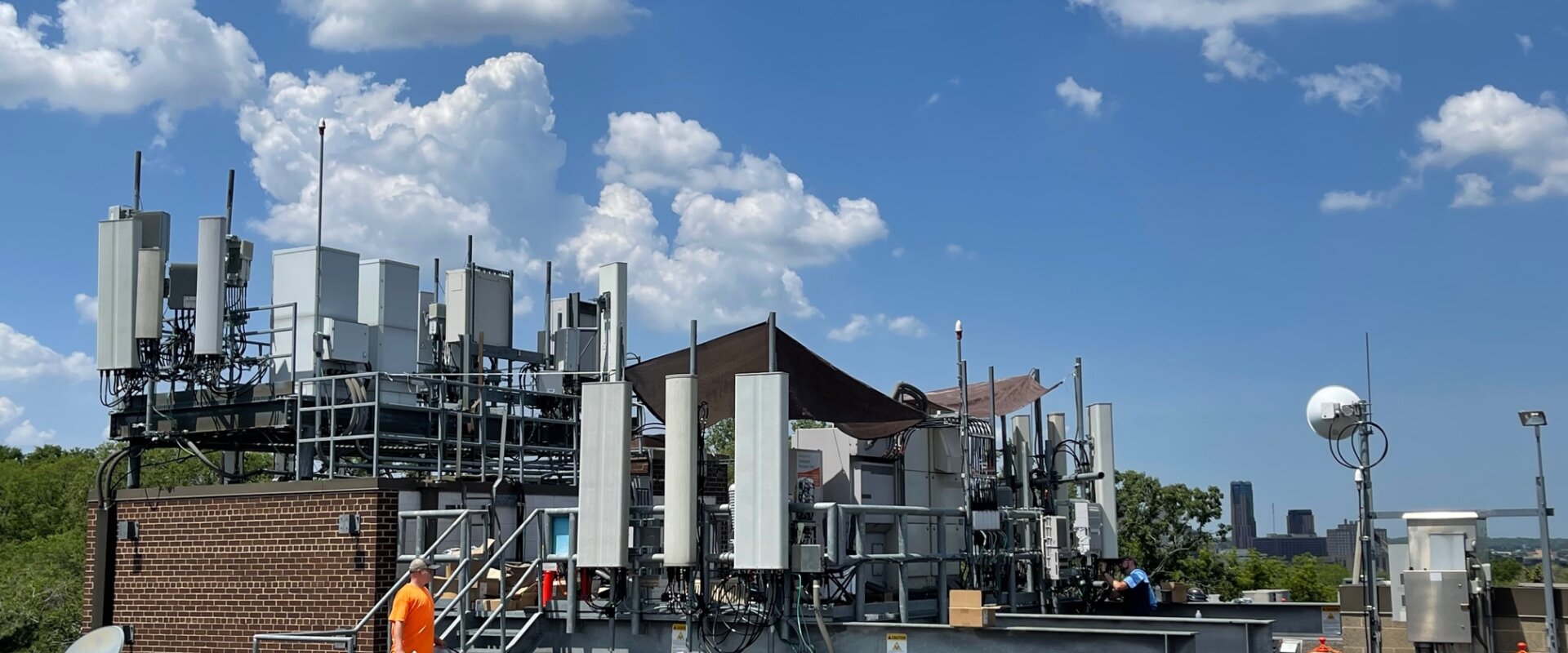
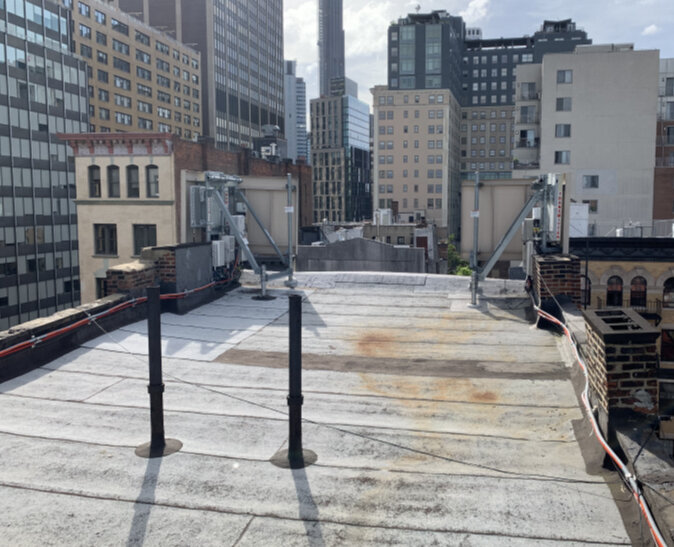
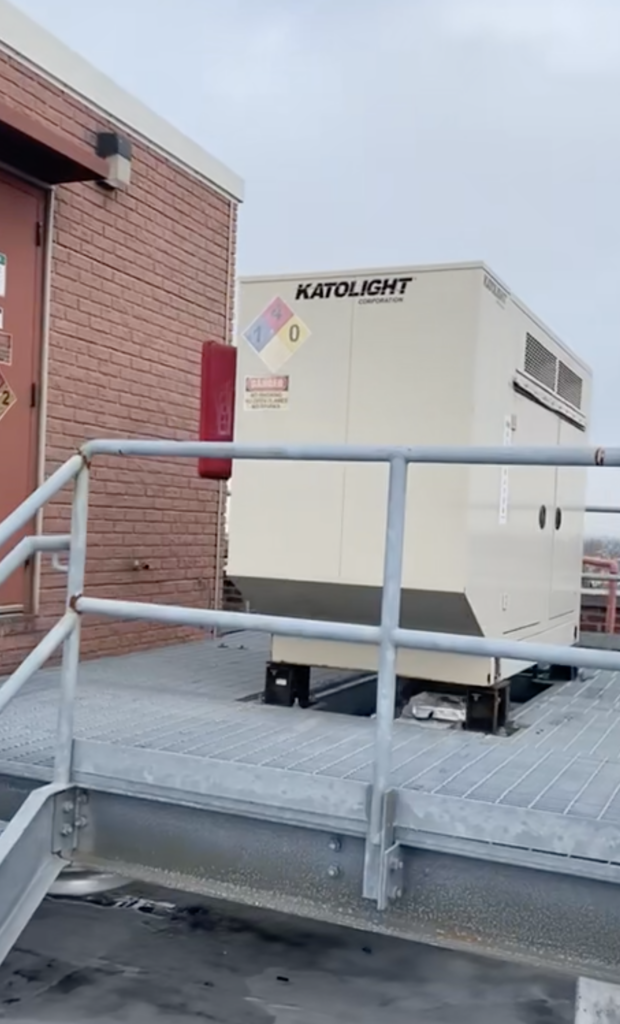
Here is a multi-carrier rooftop cell site example.

Sure, cell sites are ugly. But ask yourself… What was your life like before cell towers, or before having a smart phone device? Without cell sites, none of them would work. This rooftop is a “wireless cell site farm” outside a small city in the Northeast. The building owner leases rooftop equipment and antenna space to Verizon Wireless, AT&T, T-Mobile, and to DISH Wireless. They also used to lease space to Nextel, Metro PCS and Sprint, however due to mergers, of those cell sites were consolidated and merged into the other service provider.
What is a cell site?
A cell site is also known as a cell tower, cell phone tower, cellular tower, communication tower, or mobile base station, and connects a given wireless communication network. Cell sites are like the highways that voice and data communications flow. It’s important to note, that every cell phone tower is a cell site, but not every cell site is a cell tower, depending on what type of structure is used for mounting the antennas. For example, a rooftop cell site, where antennas are placed on an antenna sled, and weighted down on the rooftop with under blocks or sandbags, is a cell site, but it is not a cell tower. We basically define a cell site as a structure that’s equipped with antennas, transmitters, receivers, and other electronic equipment that make the transmission and reception of signals to and from cellular devices possible. These wireless telecom sites are strategically positioned in a sort of mesh, or grid, to ensure optimal coverage and network reliability within a specific geographical area, or coverage area, that’s often referred to as a “cell”.
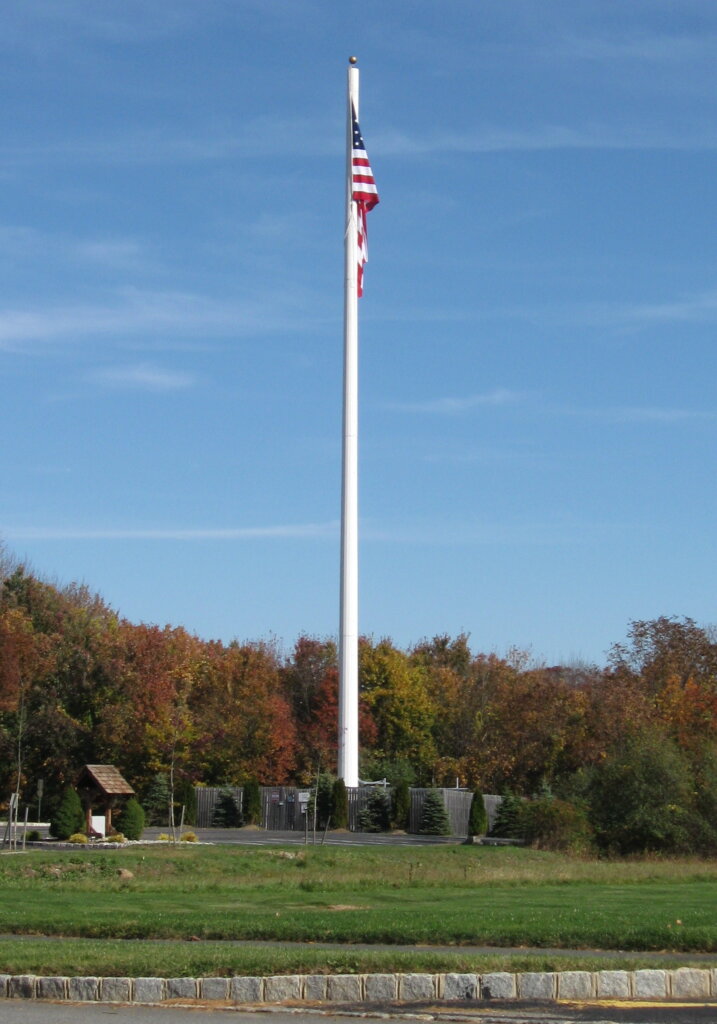
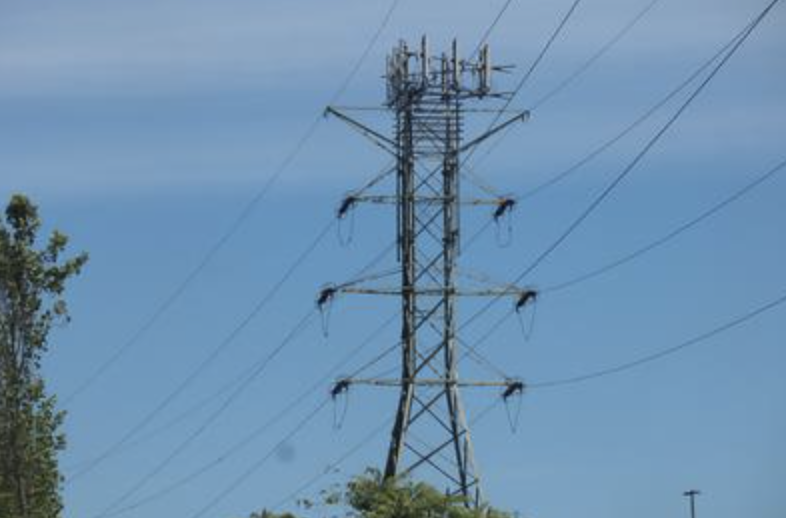
A cell site can be a cell phone tower but not all cell sites are cell towers. For example, some cell sites use other vertical real estate besides traditional towers to mount their antennas or equipment, such as water towers, electrical transmission towers, church steeples, smokestacks or rooftops. Cell sites are also getting close to the ground level with 5G technology and small cells. Cell towers can typically be anywhere from twenty to three hundred feet high, and rooftop cell sites can also be installed on rooftops of various heights. Cell tower and cell sites that exceed 200′ height are required to be lit at night by the FAA.
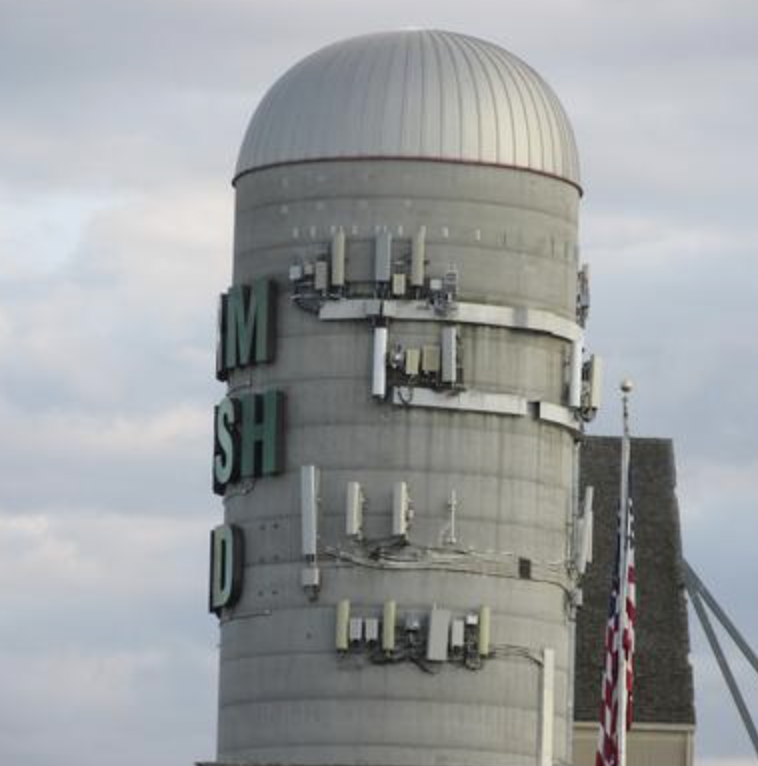
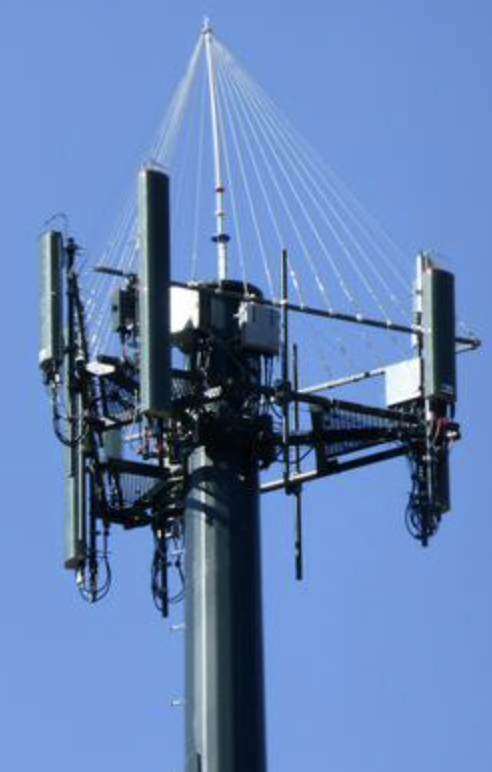
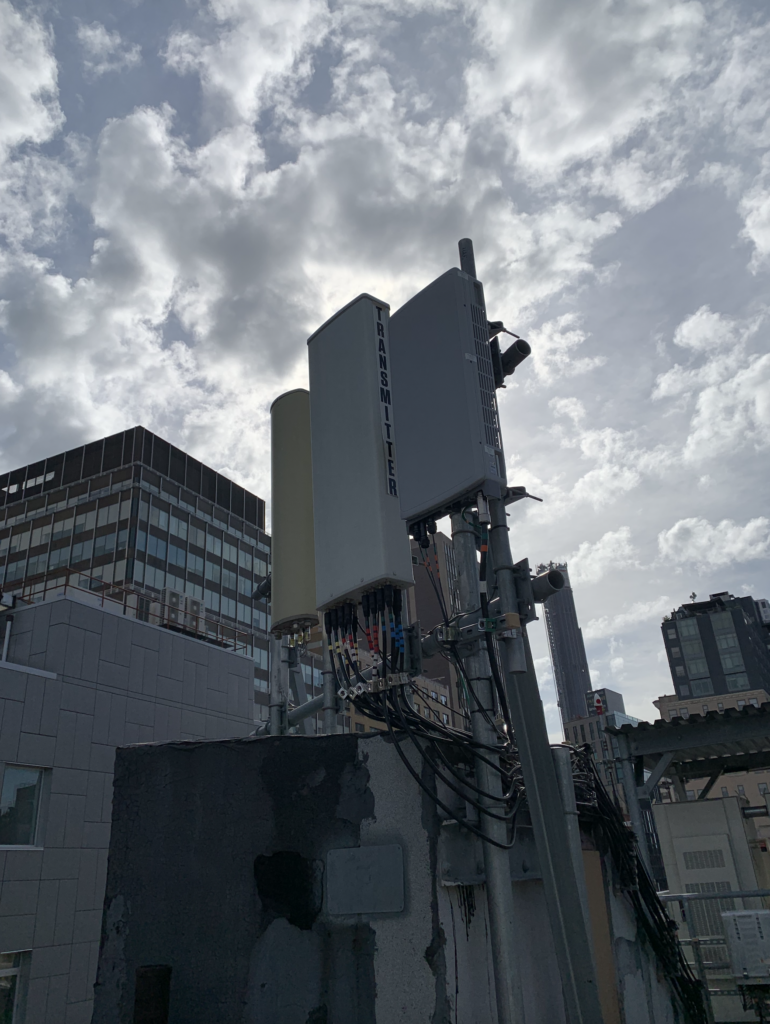
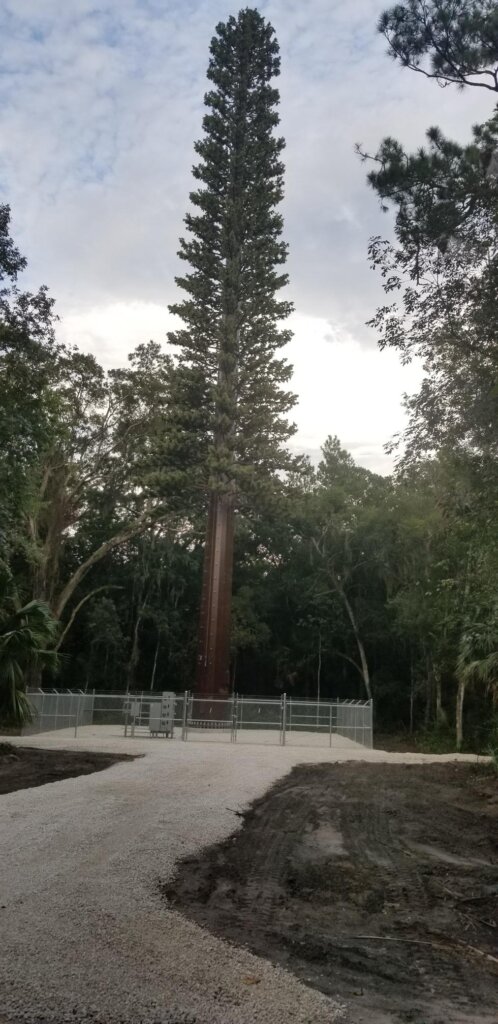






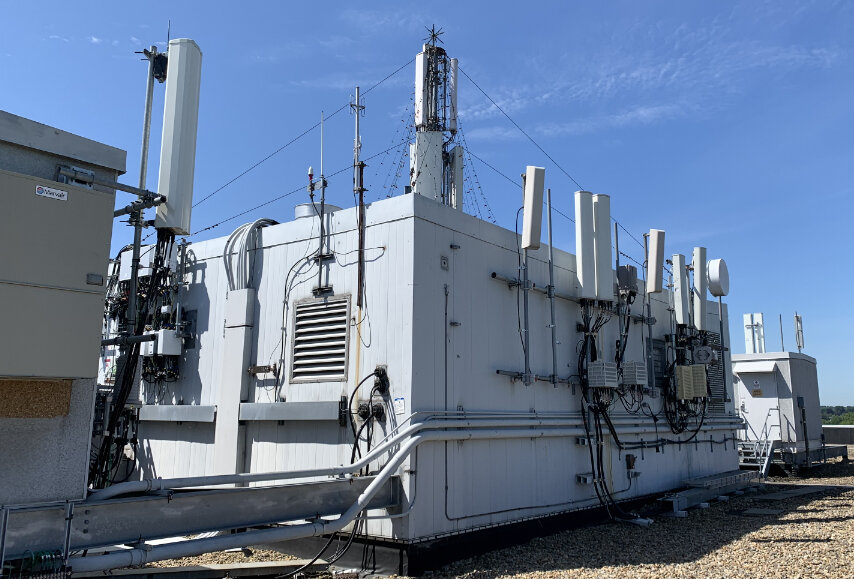
How do cell sites work?

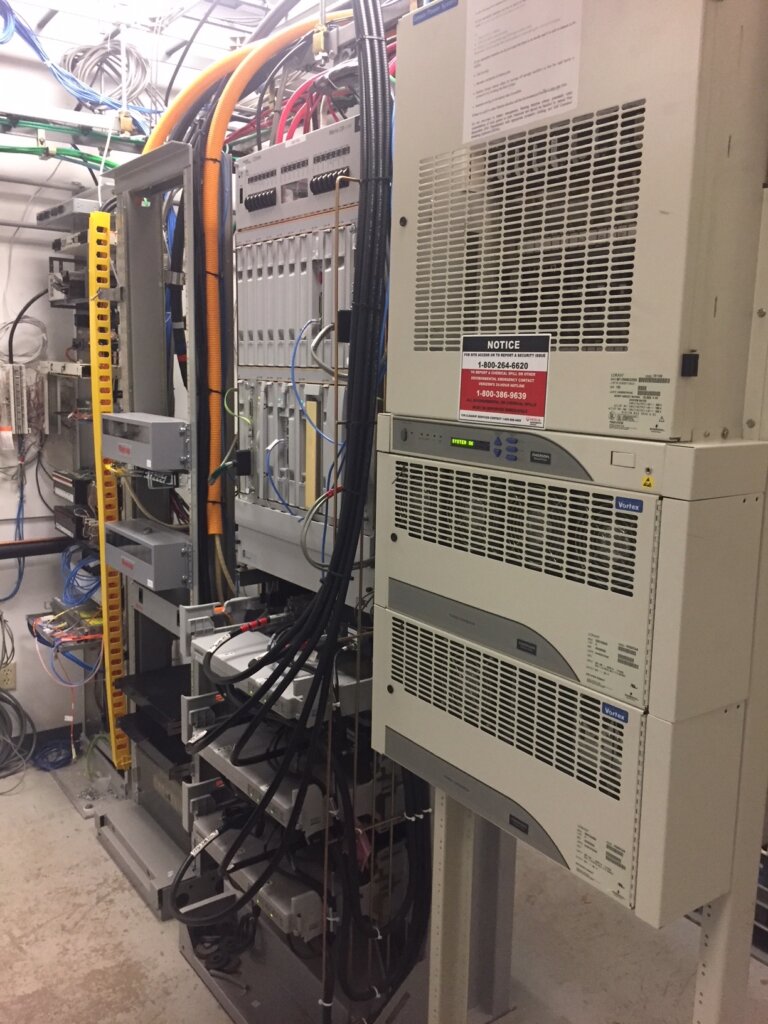
How do Cell Sites Work? It’s kind of like magic actually. Cell sites operate by connecting or “talking” with cellular devices within their coverage area. They receive signals from cellphones and transmit them to the core network infrastructure, where data is processed and routed to its destination. Similarly, they receive data from the core network and transmit it wirelessly to mobile devices. The amazing thing are the speeds of these handoffs, which happens in fractions of a millisecond.
Cell sites communicate with cellular devices through radio frequency (RF) signals. When a user initiates a call, sends a text message, or accesses the internet, their device transmits RF signals to the nearest cell site. These signals carry information encoded in electromagnetic waves, which are then received by the antennas on the cell site.
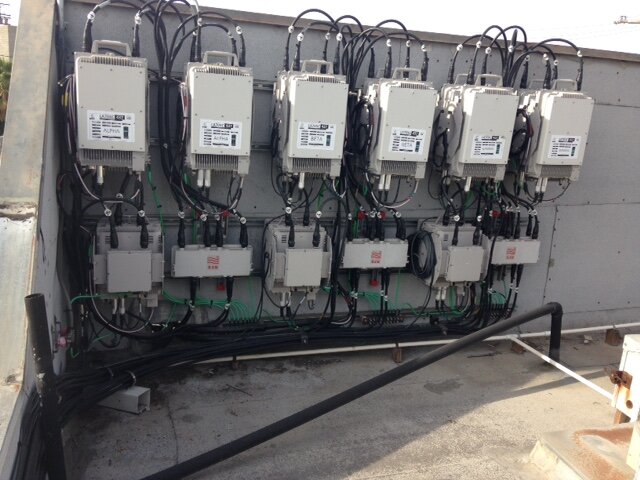
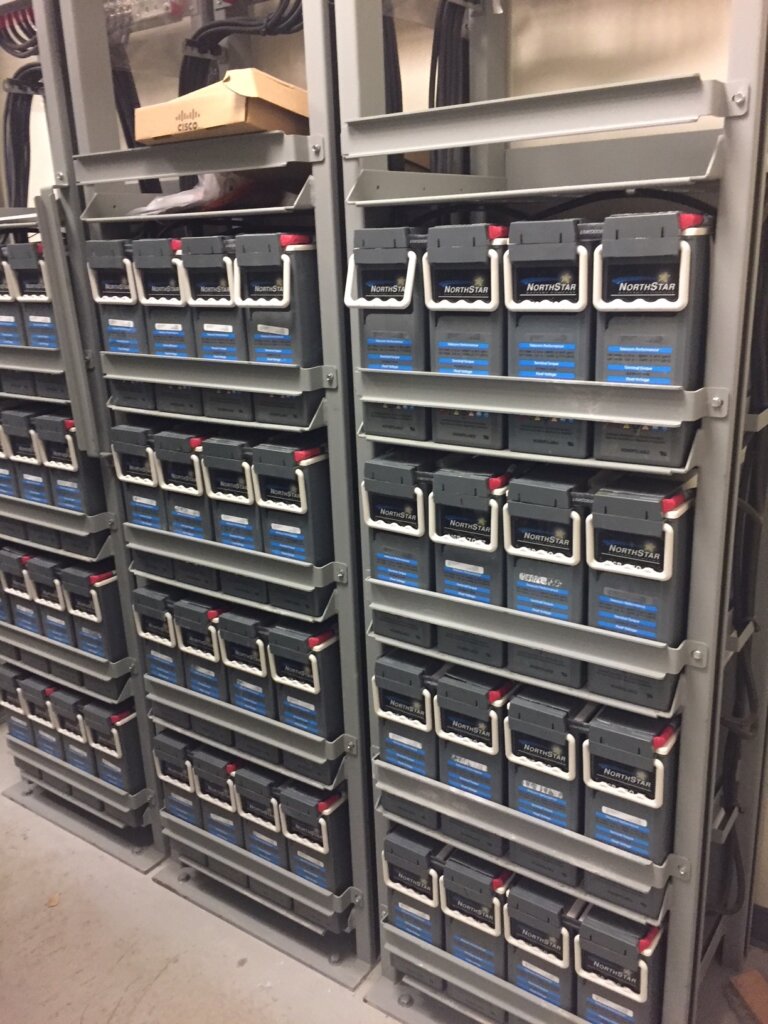
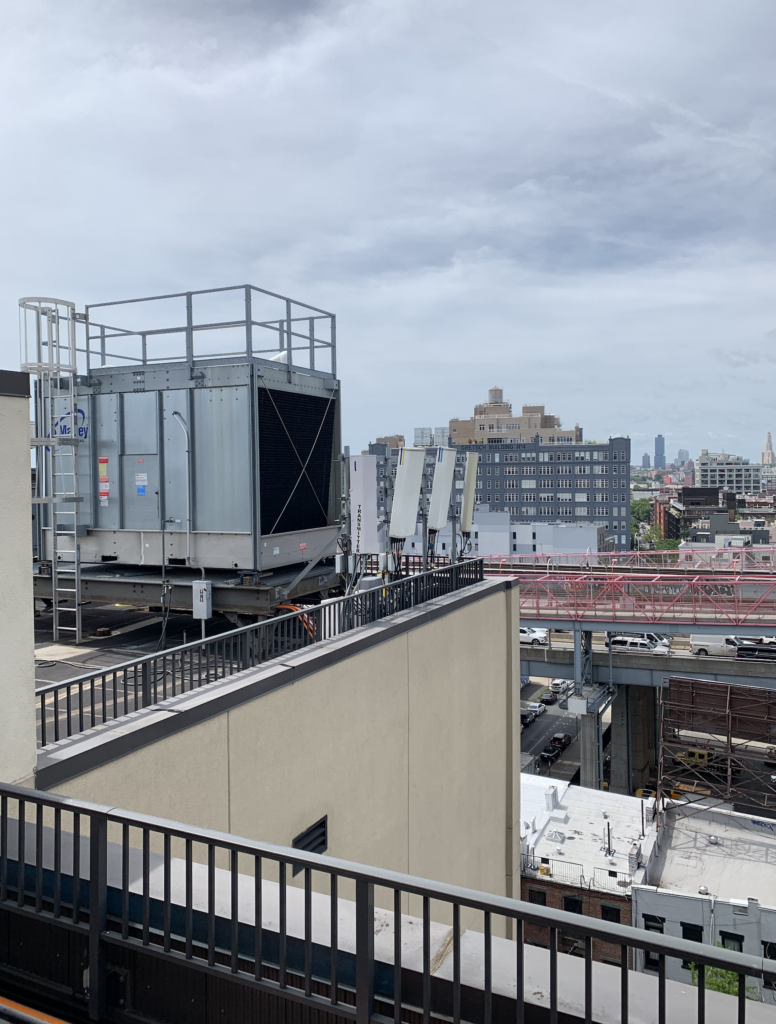
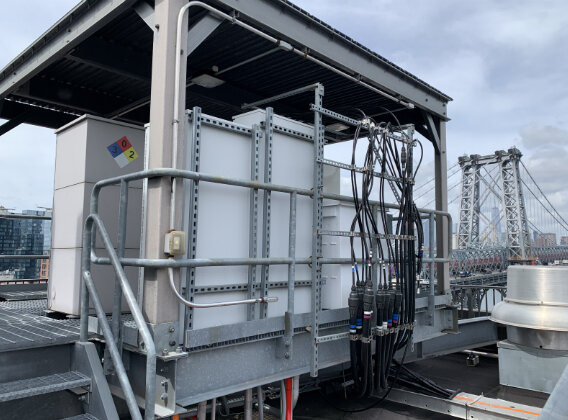






Often times on rooftops where there are multiple carriers such as T-Mobile, AT&T, DISH Wireless or Verizon Wireless sharing space, it is difficult for building owners or building managers to keep track of what a carrier is doing, or if they are in compliance with their lease agreements. Often time wireless carriers exceed the boundaries of their agreements, or puncture rooftops accidentally and end up causing hundreds of thousands of dollars worth of flooding damage to buildings.
4G and 5G Cell Sites
Fourth-generation, 4G wireless antenna cell site technology was ten times (10X) faster than 3G cellular communication, introducing faster data speeds, reduced latency, and improved network capacity compared to its predecessors. Fifth-generation 5G technology, promising even more remarkable advancements in wireless communication. While specific speed may vary, it’s not uncommon for 5G to be at least 10 times faster than 4G in terms of peak download speeds. In some cases, particularly with the deployment of millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum and advanced antenna technologies, the speed difference between 5G and 4G can be even greater, reaching up to 100 times or more. Another industry term is MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output). MIMO systems utilize multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver ends to enhance signal quality and throughput.
Types of Cell Sites You Are Likely To Find
Common types of cell sites include:
– Towers: Tall structures typically located in rural or suburban areas.
– Monopoles: Single-pole structures often used in urban environments for aesthetic reasons.
– Guyed and Lattice Towers: Structures supported by guy wires or lattice framework, respectively, providing stability and support for antennas.
– Rooftop Sites: Antennas mounted on rooftops of buildings to maximize coverage in urban areas.
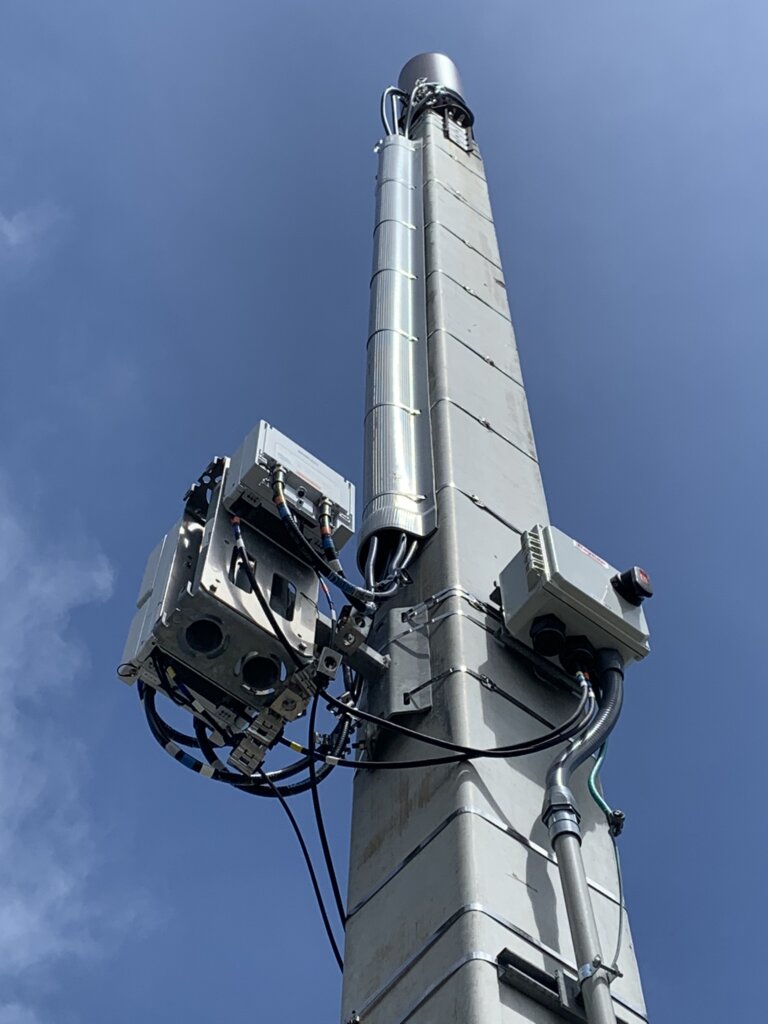
– Small Cells: Compact, low-power base stations deployed in densely populated areas to improve coverage and capacity.
– Macro cells: large traditional cell sites deployed on towers or other structures such as rooftops provide coverage to a larger geographic area.
– Small Cells: Small-scale base stations designed for indoor or outdoor use in specific locations, such as shopping malls or stadiums.
– 5G Nodes and LTE DAS: Advanced small cell and cell sites utilizing fifth-generation (5G) technology and Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) to deliver high-speed connectivity and support for multiple devices simultaneously.
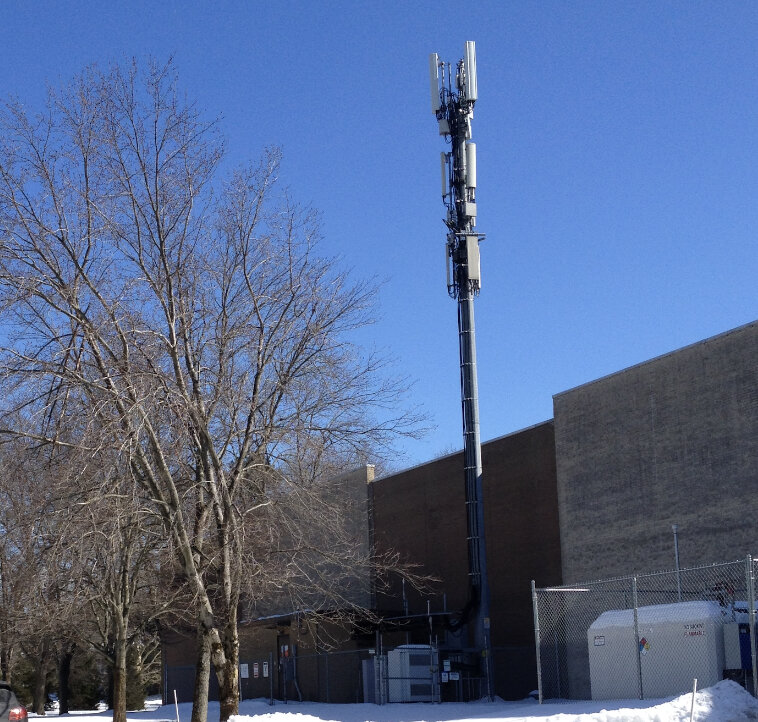






Who Own and Operate Cell Sites and Who are America’s Top Cell Site Management Companies?
In the United States, the deployment and management of cell towers are often handled by specialized companies that lease space to wireless carriers. Among the top players in this industry are:
1. American Tower Corporation: ATC a portfolio of over 181,000 cell sites globally, including approximately 43,000 cell towers in the United States.
2. Crown Castle International Corp: Crown Castle owns and operates approximately 40,000 cell towers and over 80,000 route miles of fiber optic cable across the United States, making it one of the largest tower companies in the country.
3. SBA Communications Corporation: SBA Communications owns and operates over 17,000 cell phone towers in the USA.
4. Vertical Bridge: Vertical Bridge is a privately-owned company that owns and operates over 5,000 wireless communication towers.
5. US Cellular: US Cellular is a carrier and a Cell Tower Company that owns over 4,400 cellular tower sites in the USA.
5. Verizon Wireless: Verizon Wireless is the USA’s leading carrier has well over 65,000 macro cell sites, and tens of thousands of small cell sites covering the entire USA.
6. AT&T: AT&T also operates one the USA’s second largest and most reliable wireless networks, with approximately 65,000 macro cell sites and tens of thousands of small cell sites.
7. T-Mobile US: T-Mobile operates nearly 80,000 cell sites and about half as many small cell sites in the United States.
8. Dish Wireless: Dish Wireless is the new 5G carrier on the block, the satellite TC provider because a wireless carrier as a by-product of the T-Mobile Sprint merger and has been playing catch-up with the other carriers. They are not building cell towers, rather deploying cell sites on rooftops and subleasing tower space and ground space at existing cell tower locations.
Cell Sites, Lease Agreements and Easements
Securing sites for cell site deployment involves securing and acquiring property through lease agreements between wireless carriers or cell tower companies, and property owners. Carriers and Tower Companies are given an easement to access the property and to bring the required utilities to the cell site. These lease agreements outline terms such as cell site rental payments and other business terms, access to the cell site, insurance, property taxes, hazardous materials, cell site maintenance responsibilities and restoration of the property following termination. Summaries of these leases or memorandums are recorded against the deed at the city or county a cell site is located in.
In conclusion, cell sites represent the backbone of wireless telecommunications, enabling seamless connectivity and communication between cellular devices. Without a properly structured cell site lease agreement, cell sites would be at risk of frequent relocation, and property owners can open themselves up to future problems. Tower Genius LLC is a leader in providing cell site landlords and their attorneys in the USA with specialized cell site lease consulting services.Is there a difference in cell site lease rental prices on rooftop cell sites and cell phone towers? How are they calculated? What are average cell site lease rates? If you or your attorney have common questions such as these, Tower Genius can help answer your cell site lease related questions. Our phone number is 1-888-313-9750.

The Partners of Tower Genius, Kevin Donohue and Steve Kazella have over 50 years of combined cell site infrastructure and cell tower leasing experience helping property owners with cell site related matters.
- About Tower Genius’ Cell Site Consulting Services
Tower Genius, LLC is the leading carrier-neutral cell site lease consulting firm exclusively servicing property owners, landlords, and municipalities across the United States. Kevin and Steve’s backgrounds having worked in-house and later as cell tower site acquisition subcontractors for cellular carriers to build out entire wireless networks, their knowledge of leasing cell sites on the carrier side, and working exclusively for property owners since 2008, give them the well-rounded understanding of the ins and outs of the wireless leasing industry that others simply do not have.

The Steps To Avoid When Negotiating a Cell Site Lease – FREE Guide:
Download our FREE Guide here and contact us if you require cell site lease assistance anytime with any questions relating to your cell site lease valuation, negotiation or easement sale.
Get your FREE Guide and then give us a call at 1 (888) 313-9750. We would love to discuss what your cell tower lease rental stream is worth and what you should expect to receive for it if you decide to hold onto it and renegotiate the lease or if you offer it to a Cell Tower Lease Buyout Company.
Contact Us For Help With A Cell Site Lease
Contact Us
We would love to hear from you! Please fill out this form and one of us from Tower Genius will get in touch with you shortly.


